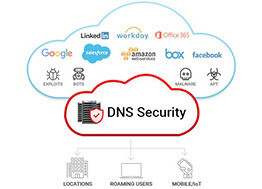
DNSSEC ensures the confidentiality of your data online, which is something that the DNS did not previously handle on its own. DNS Security Extensions digitally sign data, which guarantees its authenticity. This happens at every step in the domain name translation process to ensure proper security The DNS is an essential piece of infrastructure for the Internet as we know it today. Due to how involved it is in our day to day activity, knowing how to protect yourself against attacks that target it is vital in the modern cyber-landscape. Applying the necessary DNSSEC protocols and enforcing additional measures to safeguard your data is up to you.

Network firewalls are security devices used to stop or mitigate unauthorized access to private networks connected to the Internet, especially intranets. The only traffic allowed on the network is defined via firewall policies – any other traffic attempting to access the network is blocked. Network firewalls sit at the front line of a network, acting as a communications liaison between internal and external devices. A network firewall can be configured so that any data entering or exiting the network must pass through it – it accomplishes this by examining each incoming message and rejecting those that fail to meet the defined security criteria. When properly configured, a firewall allows users to access any of the resources they need while simultaneously keeping out unwanted users, hackers, viruses, worms, or other malicious programs trying to access the protected network.
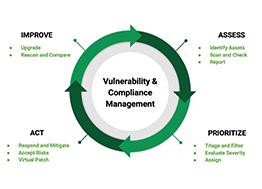
Vulnerability scanning is an inspection of the potential points of exploit on a computer or network to identify security holes. A vulnerability scan detects and classifies system weaknesses in computers, networks and communications equipment and predicts the effectiveness of countermeasures. A scan may be performed by an organization’s IT department or a security service provide, possibly as a condition imposed by some authority. An Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV), for example, is a service provider that is certified and authorized by the Payment Card Industry (PCI) to scan payment card networks. Vulnerability scans are also used by attackers looking for points of entry. A vulnerability scanner runs from the end point of the person inspecting the attack surface in question. The software compares details about the target attack surface to a database of information about known security holes in services and ports, anomalies in packet construction, and potential paths to exploitable programs or scripts. The scanner software attempts to exploit each vulnerability that is discovered